Immunolabelling
Cells grown on glass coverslips are immunolabelled prior flat-embedding. For immunolabelling, cells are fixed with PLP-fixative and permeabilized by saponin. For detection of immunolabelling, we use Fab-fragments of secondary antibodies conjugated with 1.4 nm gold particles (
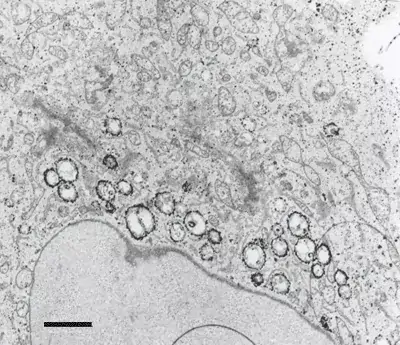
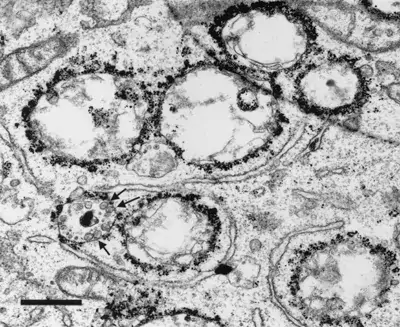
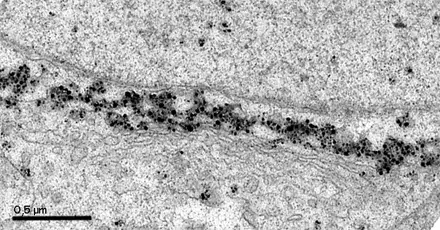
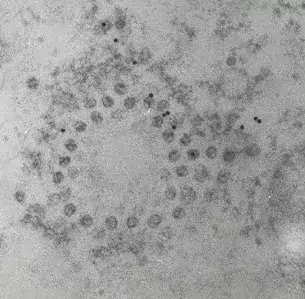
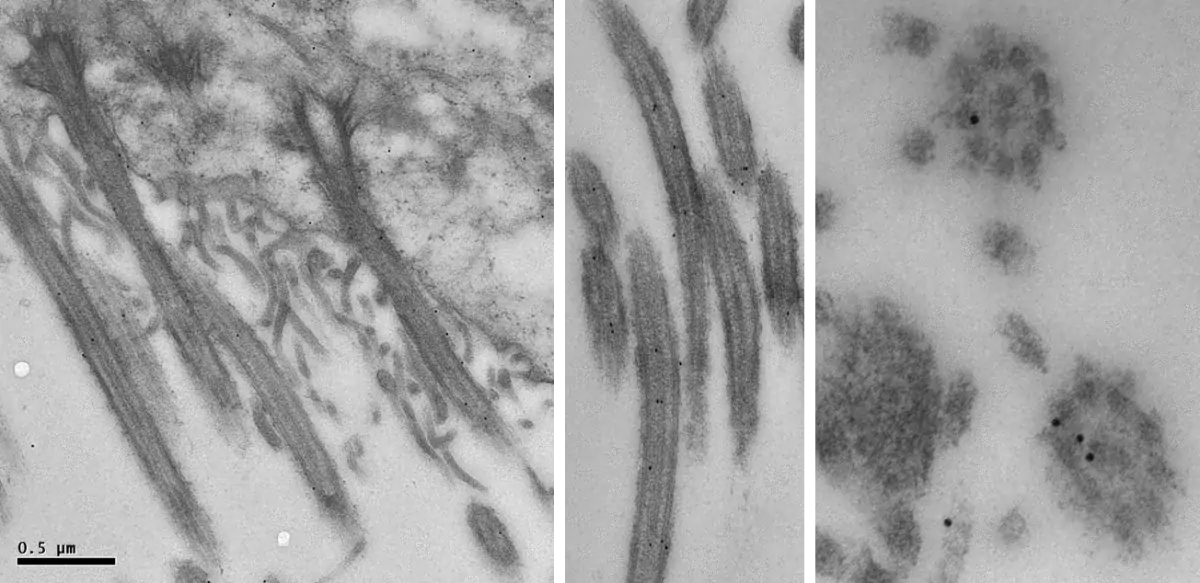
Image 1 and 2 Silver enhanced immunogold labelling of nsP1 protein in Semliki forest virus -infected HeLa-cells on the cytoplasmic side of the limiting membrane of virus-induced cytoplasmic vacuoles (CPVs). Arrows indicate spherules, which are the sites of synthesis of viral RNA. (Salonen et al., 2003, J Virol 77:1691-1702). Bars 2 µm (Image 1) and 500 nm (Image 2).
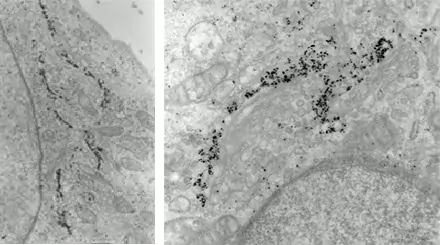
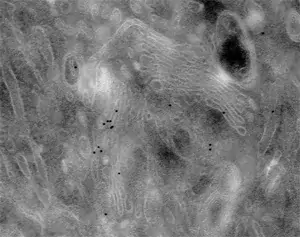
Image 3 Immunogold labelling of Galactosyl transferase enzyme localizing to trans-Golgi cisternae (left) or Golgi matrix protein GM130 localizing to the cytoplasmic side of cis and medial Golgi cisternae (right) in NRK cells (E. Jokitalo).
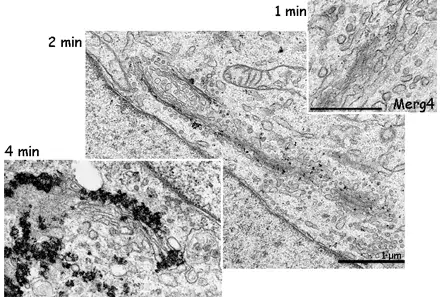
Image 4 The effect of enhancement time becomes clear when comparing these three Golgi protein labellings (E. Jokitalo).
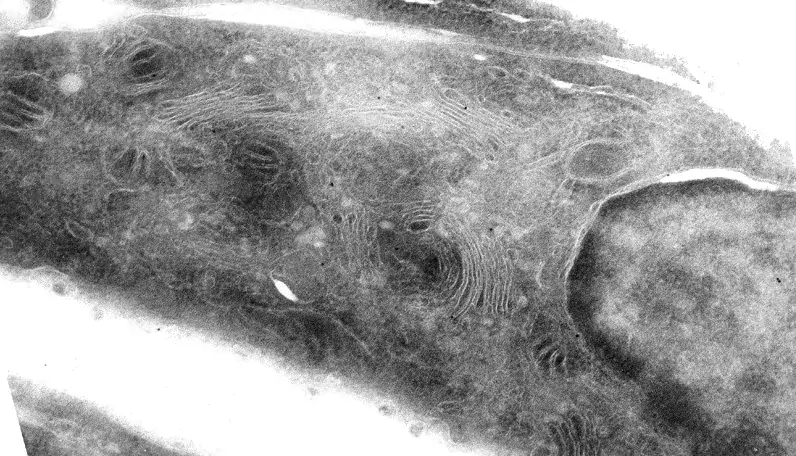
Image 5 Gold toning stabilizes the silver precipitate. Without gold toning, only some of the precipitate formed during long enhancement time persists on the section. Immunolabelling is against Golgi matrix protein GM130 on NRK-52E cells (O.Välimäki).
Cells are fixed with formaldehyde/glutaraldehyde mixture or high pressure frozen, and then embedded in Lowicryl HM20 resin (TAAB) at cold temperatures using freeze substitution method. Labelling is done on ultrathin plastic sections using secondary antibodies conjugated with 5, 10 or 15 nm gold particles (British BioCell) or protein A-conjugated with 5, 10 or 15 nm gold particles (University of Utrecht, School of Medicine, Departure of Cell Biology).
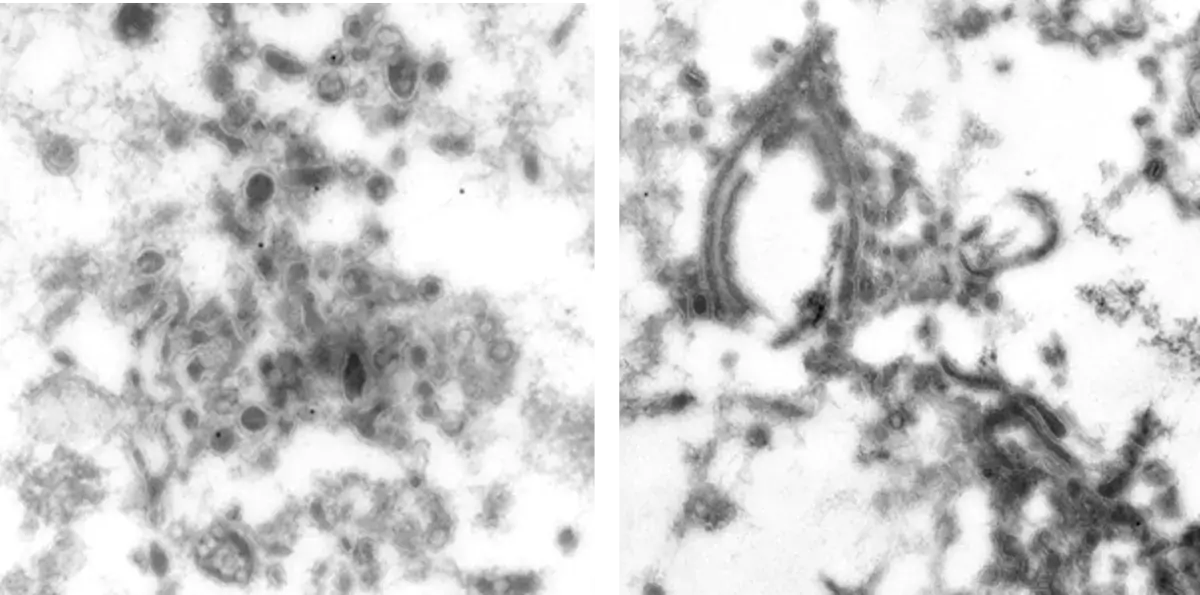
Image 1 Semliki forest virus infected cells are high pressure frozen, freeze-substituted and embedded in Lowicryl. Ultrathin sections are labelled with antibody against one of the non-structural viral proteins (E. Jokitalo).
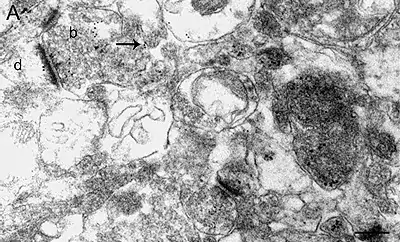
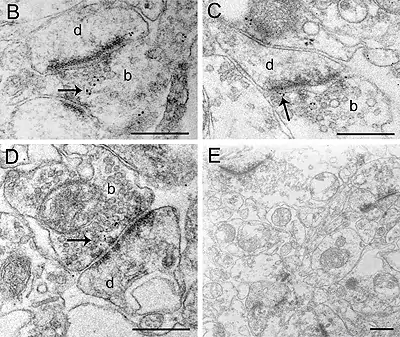
Image 2-3 Immunolabelling of α7 nAChR subunits in axon endings in the ventral tegmental area of mouse brain. The mice were perfusion fixed, and tissue slices were slam-frozen using metal mirror freezing device, and embedded in Lowicryl using freeze-substitution. (Pakkanen et al., 2005, Eur. J. Neurosci. 21:2681-2691). Bars 500 nm.
Cells are
- fixed with formaldehyde/glutaraldehyde mixture
- embedded in gelatine
- infiltrated with sucrose for cryoprotection
- frozen by immersion in liquid nitrogen
Ultrathin sections are cut with cryo-ultramicrotome at -120 °C and picked on carbon/pioloform-coated grids. Sections on grids are immunolabelled using secondary antibodies conjugated with 5, 10 or 15 nm gold particles (British BioCell) or protein A-conjugated with 5, 10 or 15 nm gold particles (University of Utrecht, School of Medicine, Departure of Cell Biology).
Image 1 NRK-cells immunolabelled with monoclonal antibody against Golgi matrix protein GM130 (E. Jokitalo).