Cytochemical staining of HRP-tagged proteins or endocytosed HRP
HRP catalyzes an enzymatic reaction that yields an insoluble reaction product that can be made electron dense with the addition of osmium. Substrates in this reaction are hydrogen peroxidase and 3-3' diaminobenzidine (DAB,
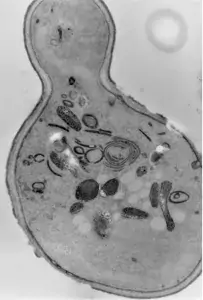
Image 1 Cytochemical staining of yeast S. cerevisiae Sec7 cells expressing Hsp150Δ-HRP reveals Golgi elements (L. Karhinen).
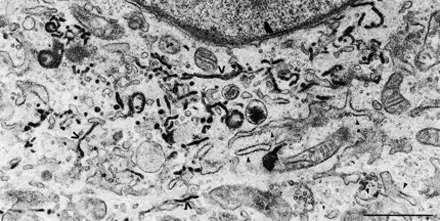
Image 2 and 3 Cytochemically stained endoplasmic reticulum of NRK-52E cells expressing a construct where HRP is tagged with signal sequence and ER retention signal KDEL during interphase (upper, Jokitalo et al., 2001, JCB 154:317-330) or anaphase (lower, E. Jokitalo).
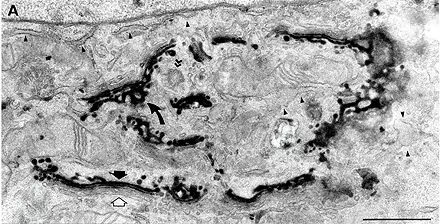
Image 4 Cytochemical staining of NRK-52E cells stably expressing Sialyl transferase-HRP chimera. The stain is present in the trans-cisternae (black arrow) and trans Golgi network (curved arrow; Jokitalo et al., 2001, JCB 154:317-330).
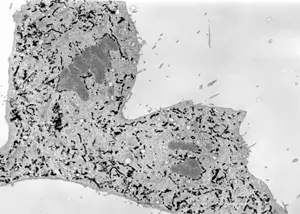
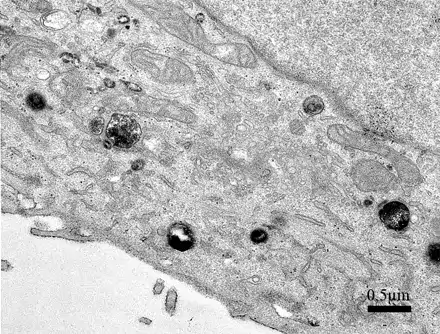
Image 5 HRP (e.g. Type II, Sigma P-8250) is added to the growth medium, and cells take it in by fluid phase endocytosis (pinocytosis). Cells can be fixed, or HRP-containing medium can be replaced with normal medium and HRP inside the cells is allowed to be transported further along the endocytotic pathway. Using different pulse-chase times, the HRP staining can be detected in early or late endosomes or lysosomes, or even in trans Golgi network. In this experiment, cells were incubated with HRP-containing medium for 15 minutes and fixed (O. Rämö & L. Mattinen, EM-course 2007).